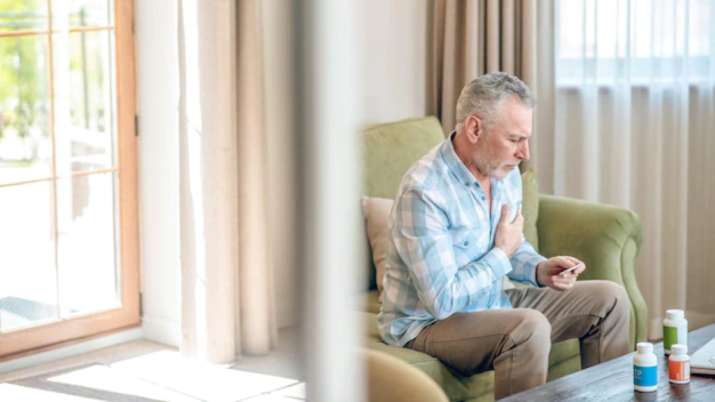
Poor diabetes control, sedentary lifestyle and being overweight are significant causes of heart attacks among Indians, a research study has found.
Controlling these risk factors is as important as conventional risk factors, the large study, “Metabolic Risk Factors in First Acute Coronary Syndrome” (MERIFACSA), addressing the risk factor issues in the Indian population was published in the Indian Heart Journal.
This study, conducted by a team of researchers across the country led by Principal Investigator, Senior Cardiologist Dr. B. Hygriv Rao of KIMS Hospital, Hyderabad, involved 15 major tertiary cardiology hospitals from New Delhi to Thiruvananthapuram.
Over a period of 2 years, 2,153 patients were recruited and compared to 1,200 from the control population. The patients recruited came from different economic strata and represented both the rural and urban population.
The average age of the patients was 56 years old and 76% were men. It has again been shown that despite improvements in health care over the past 20 years, an even younger age group suffers from heart attacks.
Up to 66% of men and 56% of heart attacks in women were under the age of 60, while a third of men and a quarter of women had heart attacks before the age of 50 and 10% of heart attacks was under 40 years old. .
It is well known that smoking, hypertension, diabetes and high LDL cholesterol are risk factors for heart attacks. It is expected that 93% of patients will have these risk factors. Other risk factors are known to be important, but are not given as much importance. These are overweight (high body mass index, high waist to hip ratio), poor diabetes control, high triglycerides and HBA1C, and a sedentary lifestyle (HDL) . These factors were present in more than 95% of patients who suffered a heart attack.
Read: Do apple cider vinegar and black pepper help with weight loss? Myth or reality
The study showed that controlling these risk factors is as important as conventional risk factors.
A third of the patients had HBA1C in the pre-diabetic range (6-6.5), showing that preventive measures against heart attacks must begin before the onset of clinical diabetes. The study points out that to prevent heart attacks in India, obesity prevention, aggressive control of diabetes and regular exercise are important.
Read: This is Serious! Smoking can lead to thicker, weaker hearts, study finds
“Obesity, sedentary lifestyle and lack of aggressive diabetes treatment is a significant gap in our heart attack prevention treatment in India. The risk factor modification practiced by doctors in India is not comprehensive unless these factors are addressed seriously on a large scale,” Hygriv Rao said.
At the individual level, people need to follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly to avoid becoming overweight (target body mass index 23-25 and waist-hip index below 0.9. Second, profile annual lipid monitoring and screening for diabetes by doing HBA1C Diabetics should aim for an HBA1C of less than 7. As heart attacks occur in the younger population, these preventive measures should be initiated early, such as from the age of 20.
Specific measures at the national level are large-scale screening programs to identify diabetes by estimating HBA1CA rather than blood glucose alone, and to advise patients to aggressively achieve a value below 7 in the diabetic population. Promote, through educational campaigns, the importance of a healthy diet and regular physical activity to prevent obesity and increase good cholesterol (HDL).
Latest health news